DISASTER RECOVERY IN SAP
Disaster Recovery in SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) refers to the set of procedures, processes, and technologies put in place to recover and restore critical SAP systems and data in the event of a catastrophic event or unexpected disaster. The primary goal of a disaster recovery plan for SAP is to minimize downtime, data loss, and business disruption in the face of disasters such as natural disasters, hardware failures, data corruption, or cyberattacks.
SAP ASE, or SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise, is a high-performance relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by SAP. It was previously known as Sybase ASE (Adaptive Server Enterprise) before being acquired by SAP in 2010. SAP ASE is designed to provide efficient and reliable data management for mission-critical business applications.
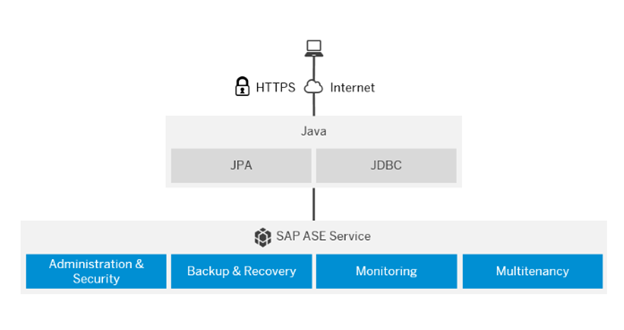
The magnitude of a disaster is unpredictable. This may include that a data center cannot be restored in a reasonable time and new infrastructure needs to get set up at a different location. This might require the purchase and setup of new hardware. Hence we cannot guarantee any fixed recovery timelines.
STEPS OF DATA RECOVERY IN SAP
Recovering data through disaster recovery in SAP involves a series of steps and preparations to ensure that critical data and systems can be restored after a disaster or unexpected event. Here’s a general guideline for recovering data in SAP through disaster recovery:
- Create a Disaster Recovery Plan:
Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan for your SAP systems. This plan should outline the procedures, responsibilities, and resources needed to recover data and applications in the event of a disaster.
- Data Backup and Replication:
Regular Backups: Implement a robust data backup strategy for your SAP systems. Regularly back up all critical data and configurations. This may involve full backups, differential backups, and transaction log backups.
A full data backup is done once a day. Log backup is triggered at least every 30 minutes. The corresponding data or log backups are replicated to a secondary location at least every 24 hours. Backups are kept (complete data and log) on a secondary location for the last 14 days. Backups are deleted afterwards.
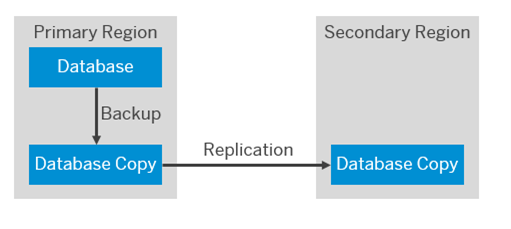
Data Replication: Set up data replication to mirror data to an off-site location in real-time or near-real-time. This ensures that even in the event of a complete site failure, data is available for recovery.
- High Availability and Failover Systems:
High Availability Configuration: Configure your SAP systems with high availability solutions. This involves maintaining secondary systems or clusters that can take over in case the primary system fails.
Failover Procedures: Define procedures for failing over to secondary systems or data centers. Test these procedures to ensure a smooth transition in case of a disaster.
- Disaster Recovery Site:
Establish a Disaster Recovery Site: Maintain an off-site disaster recovery site equipped with the necessary hardware, software, and infrastructure to host your SAP systems in case of a disaster.
Since backups are kept on a secondary location for 14 days, recovery is only possible within a time frame of 14 days.
- Testing and Drills:
Regular Testing: Conduct regular disaster recovery testing and drills to ensure the plan’s effectiveness. Simulate various disaster scenarios and assess the recovery process.
- Data Encryption and Security:
Data Security: Implement encryption and security measures for both data in transit and data at rest. Protect data during the backup and replication processes.
- Documentation and Procedures:
Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation that includes detailed step-by-step procedures for data recovery, contact information, and roles and responsibilities.
Chain of Command: Define a clear chain of command for disaster recovery operations, including who is responsible for decision-making during recovery.
- Communication and Notification:
Communication Plan: Develop a communication plan to ensure that relevant stakeholders are informed promptly during a disaster. This includes IT staff, management, and third-party service providers.
- Cybersecurity Preparedness:
Cybersecurity Measures: Strengthen cybersecurity measures to protect data during disaster recovery. This includes monitoring for cyber threats and potential attacks during recovery.
- Regular Updates and Maintenance:
Regular Maintenance: Keep your disaster recovery plan, systems, and procedures up to date to align with changes in your SAP environment and evolving threats.
- Legal and Compliance Considerations:
Legal and Compliance Compliance: Ensure that your disaster recovery plan and data recovery procedures comply with industry-specific regulations and legal requirements.
By following these steps and incorporating data backup into your disaster recovery plan, you can help ensure that your SAP data is protected and can be quickly restored in case of a disaster or system failure. Regularly reviewing and updating your backup strategy is important to adapt to changing business needs and emerging threats. Read More.

 RECOGNISED WORLD OVER SOLUTIONS
RECOGNISED WORLD OVER SOLUTIONS
 Find out how BSC GLOBAL digitally transformed P2P cycle for worlds renowned brand in Automobile
Find out how BSC GLOBAL digitally transformed P2P cycle for worlds renowned brand in Automobile









