Privileged Access Management in SAP S/4HANA Cloud: An In-Depth Guide
In the rapidly evolving realm of cloud computing, managing privileged access is paramount for ensuring security and operational integrity. SAP’s rollout of Privileged Access Management (PAM) for SAP S/4HANA Cloud, part of the SAP Cloud Identity and Access Governance (IAG) release 2302, represents a significant step forward in access control. This feature enhances security and compliance within SAP environments. This blog will delve into the essential steps and best practices for implementing PAM in SAP S/4HANA Cloud.
Understanding the Basics
Privileged Access Management (PAM) in SAP S/4HANA Cloud is a critical component of cybersecurity and compliance, acting as the foundation of secure cloud operations. But what exactly is PAM, and why is it so crucial in the SAP ecosystem? PAM is a security solution designed to monitor and control elevated (‘privileged’) access within an IT environment. Privileged accounts are those with administrative or specialized access to critical systems. In SAP S/4HANA Cloud, these accounts might include system administrators, superusers, or any account with access to sensitive data and controls.
Privileged or Emergency Access Management in SAP refers to the secure granting and monitoring of temporary, high-level access to critical systems and data during exceptional situations, ensuring strict controls, auditability, and accountability. This access is usually granted to authorized personnel for urgent tasks and is closely managed to minimize security risks.
The Benefits of PAM
- Enhanced Security: PAM ensures that only authorized personnel have access to critical systems, reducing the risk of security breaches.
- Audit and Compliance: It provides detailed logging and tracking of privileged activities, which is crucial for audits and regulatory compliance.
- Least Privilege Principle: PAM enforces the principle of least privilege, granting users only the access necessary for their role, minimizing the potential for unauthorized access or actions.
Key Terminologies in PAM
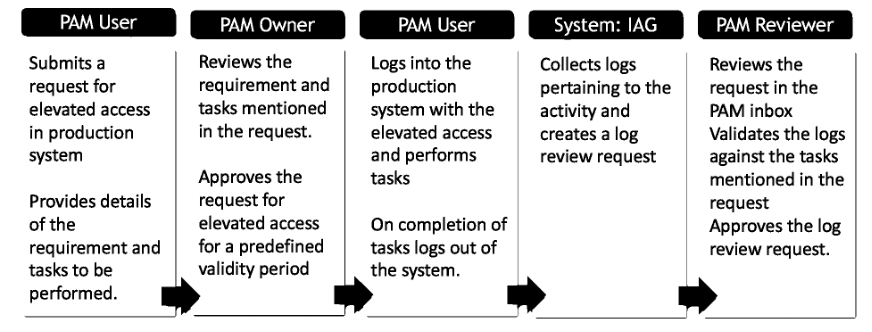
- PAM User: The IT Support User who requires elevated access.
- PAM ID: The User ID with elevated privileges.
- PAM Approver: The person(s) who approves the assignment of PAM IDs to PAM Users.
- PAM Reviewer: The person(s) who reviews the log requests and investigates any discrepancies between intended and actual usage.
Implementation Steps
- Client Authentication Setup
Create a client ID and secret for the S/4HANA application in Identity Authentication (IAS). This step is crucial for establishing a secure connection.
- Destination Creation in BTP
Next, create a destination in the Business Technology Platform (BTP) for PAM in the IAG Subaccount.
- Privileged Access IDs Creation
Set up privileged access IDs in PAM on IAG. This is a critical step in the implementation process.
- Provisioning Job Execution
Run the provisioning job on IAG to ensure all configurations are in effect.
Prerequisites
Before implementing PAM in SAP S/4HANA Cloud, certain foundational steps must be completed:
- The IPS_PROXY destination must be set as per SAP documentation.
- The S/4HANA Cloud application setup must be completed as per SAP documentation.
- Worker IDs for the PAM IDs must be created using the Manage Workforce app in S/4HANA Cloud.
- Business roles for PAM must be defined in IAG.
- PAM access must be provided using BTP role collections for PAM to administrators, approvers, reviewers, and end users (Pre-delivered role collection CIAG_Privileged_Access).
- The Access Request workflow for PAM must be set up as per SAP documentation (Request Type: PAM and PAMREVIEW).
Summary
Implementing Privileged Access Management (PAM) in SAP S/4HANA Cloud is essential for maintaining a secure and compliant environment. By following the outlined steps, including setting up client authentication, creating destinations in BTP, configuring privileged access IDs, and executing provisioning jobs, organizations can effectively manage elevated access. Ensuring prerequisites such as IPS_PROXY destination setup, S/4HANA Cloud application setup, and proper role definitions are in place is crucial for a smooth implementation. PAM not only enhances security and compliance but also enforces the least privilege principle, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access or actions. Read More

 RECOGNISED WORLD OVER SOLUTIONS
RECOGNISED WORLD OVER SOLUTIONS
 Find out how BSC GLOBAL digitally transformed P2P cycle for worlds renowned brand in Automobile
Find out how BSC GLOBAL digitally transformed P2P cycle for worlds renowned brand in Automobile











